Namaste, welcome to our blog Dr. Health Factory, the blog aims to share basic knowledge about facts related to human beings to all the viewers irrespective of their profession, age, and gender.
In this article, we will share detailed information on blood-related disorders when the level of blood components increases or decrease. And if you are interested in more articles, then make sure to comment with us below.
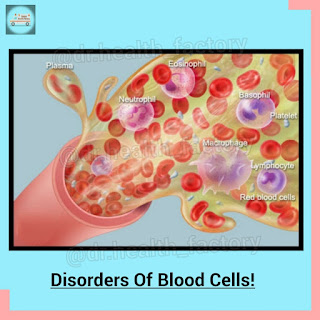
Blood:
(Average range of blood plasma is 2.8-3.2 liters per liter of blood)
- The increased volume of plasma in the blood is called hypervolemia.
- It occurs when plasma levels increase more than 3.2 liters per liter of blood.
- A decrease in the volume of plasma in the blood is called hypovolemia.
- It occurs when plasma levels decrease less than 2.8 liters per liter of blood
Red Blood Cells:
(Average range of RBCs in human blood is 4.7-6.1 million cells per cubic mm of blood)
1. Polycythemia:
- An increased volume of RBCs count in the blood results is called polycythemia.
- It occurs when the RBC count increases more than 6.5 million cells per cubic mm of blood.
- A decrease in the RBCs count is called anemia.
- It occurs when the RBC count decreases by less than 4 million cells per cubic mm of blood.
White Blood Cells:
(Average range of WBCs count in the blood is 4,300-11,000 cells per cubic mm of blood).
- An increase in the WBCs count in the blood is called leukocytosis.
- It occurs when the WBCs count increases more than 11,000 cells per cubic mm of blood.
- A decrease in the WBCs count in the blood is called leukopenia.
- It occurs when the WBCs count decreases by less than 4,000 cells per cubic mm of blood.
Causes: Autoimmune disorders, immune system disorders, cancer, infections (HIV and Tb), malnutrition, bone marrow damage or disorders, etc.
Results: Body aches, sores, sore throat, breathing difficulties, cough, fever, profusely sweating, etc.
Treatment: consuming citrus fruits, food rich in protein (poultry and meat), zinc supply as it helps in increasing the production of WBCs and T-cells, etc.
(Average range of platelets count in the blood is 1.5-4 lakh per cubic mm of blood).
1. Thrombocytosis:
- An increase in the platelet count in the body is called thrombocytosis.
- It is also called essential thrombocythemia.
- It occurs when the platelet count increases more than 4 lakh cells per cubic mm of blood.
- A decrease in the platelet count in the blood is called thrombocytopenia.
- It occurs when the platelet count decreases less than 1.5 lakh per cubic mm of blood.
If you are interested, you can follow us on Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter through the links provided on the home page, so that you can get immediate notification of our latest updates.











.png)



0 Comments
If you have any queries related to this article, let us know in the comment section.