Welcome to drhealthfactory, your comprehensive guide to wellness, health, and living your best life. At drhealthfactory, we believe in empowering individuals with the knowledge and resources they need to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Clotting Time:
Clotting Time is defined as the time lag from the onset of bleeding to the appearance of first fibrin thread at the injured area.
Clotting Time is basic test to determine the normal hemostatic process. There are few methods to measure the clotting time:
- Capillary Tube Method
- Lee And White's Method
- Slide Method
- Alcohol spirit
- Cotton
- Gloves
- Sterile lancet or needle
- Capillary tube
- Stopwatch
- Clean the finger tip with alcohol swab.
- Finger prick should be made with proper precautions to achieve a spontaneous blood flow.
- Immediately start the stopwatch after pricking is done.
- Free flowing blood should be collected in a capillary tube about 4 inches.
- Slowly break the capillary tube after 3 minutes about 1 cm in length once in every 30 seconds till the fibrin thread is seen between the two ends of the tube.
- Stop the stopwatch when you notice the fibrin thread.
- Note the time and this time indicates the clotting time.
- Syringe and needle
- Alcohol spirit
- Cotton
- Test Tube
- Cuff
- Water bath
- Gloves
- Test Tube Holder
- Stopwatch, etc.
- Tie a cuff to the forearm 4 fingers (4-5 cms) above the elbow joint.
- Clean the area to be punctured with alcohol swab to prevent septic.
- With the help of syringe and needle puncture the skin to collect 3 ml of blood.
- Soon after collecting the sample stopwatch should be started immediately.
- Add 1 ml of collected blood sample each into 3 different clean and sterile test tubes without anticoagulants.
- Place the test tubes in a water bath.
- Then 3 minutes later, slowly tilt the tubes one by one every 30 seconds.
- Clotting time is measured by noticing the test tubes at the time when blood doesn't spill after tilting.
- Taking the average of three test tubes clotting time is derived.
- Alcohol spirit
- Cotton
- Sterile Glass Slide
- Sterile needle or lancet
- Gloves
- Stopwatch
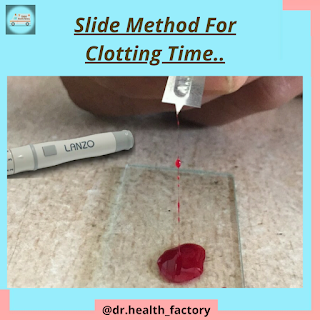
- The area to be pierced or pricked should to cleaned using alcohol swab.
- Prick the finger tip using a sterile needle or lancet.
- Then add few drops of blood on a clean glass slide placed on a flat surface.
- Start the stop watch immediately after adding blood sample to the slide.
- Keep the slide aside for 2-3 minutes.
- Then dip the needle into the blood sample on a slide and lift it up to detect fibrin thread.
- This should be repeated every 30 seconds until a fine fibrin thread appears between blood sample and needle.
- Stop the stopwatch after fibrin thread appears and note the time.
- This method is simple and easy compared to other two methods.
- Protein C Or Protein S deficiency
- Antithrombin III deficiency
- Pregnancy
- Prothrombin Gene Muttion
- Hormone Replacement Therapy
- Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome
- Aspetic technique should be used during skin puncture.
- Note the time correctly.
- Use of sterile needle, syringe, or lancet.
Thank you for spending your time and showing interest in reading our article, hope you follow, share, and comment on this article.
If you are interested, you can follow us on Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter through the links provided on the home page, so that you can get immediate notification of our latest updates.









.png)



0 Comments
If you have any queries related to this article, let us know in the comment section.